SSH (Secure Shell) is a powerful protocol that allows users to securely connect to remote servers or devices from their Macs without the need for third-party tools. Whether you're a developer, system administrator, or simply someone who wants to manage remote systems, SSH is an essential tool. This article will guide you through the process of setting up and using SSH remote on your Mac without installing additional software.
In today's digital world, understanding how to use SSH can significantly enhance your ability to manage remote systems securely. Whether you're troubleshooting issues, transferring files, or deploying applications, SSH provides a secure and efficient way to interact with remote servers.
By following this guide, you'll learn step-by-step instructions, tips, and best practices for using SSH remote on your Mac. Let's dive in and explore how you can harness the power of SSH without relying on third-party tools.
Read also:Unveiling The World Of Movierulescom Your Ultimate Movie Destination
Table of Contents
- Introduction to SSH
- Why Use SSH on Mac?
- Preparing Your Mac for SSH
- Connecting to a Remote Server
- Configuring SSH Settings
- Advanced SSH Features
- Securing Your SSH Connection
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Using SSH for File Transfer
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to SSH
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a cryptographic network protocol designed to provide secure communication over unsecured networks. It is widely used for remote system administration, file transfers, and secure command execution. One of the key advantages of SSH is its ability to encrypt all data transmitted between the client and server, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
For Mac users, SSH is pre-installed and ready to use without the need for third-party tools. This makes it an ideal choice for anyone looking to manage remote servers or devices securely and efficiently.
Key Features of SSH
- Encryption of all data transmitted between client and server.
- Authentication mechanisms to ensure secure access.
- Support for various commands and file transfer protocols.
Why Use SSH on Mac?
Using SSH on a Mac offers several advantages, including:
- Security: SSH encrypts all data, making it difficult for attackers to intercept sensitive information.
- Convenience: With SSH pre-installed on macOS, you can connect to remote servers without installing additional software.
- Efficiency: SSH allows you to execute commands and transfer files quickly and securely, saving time and effort.
Whether you're a developer working on remote projects or a system administrator managing servers, SSH is an indispensable tool for anyone working with remote systems.
Preparing Your Mac for SSH
Before you can use SSH on your Mac, you need to ensure that your system is properly configured. Follow these steps to prepare your Mac for SSH:
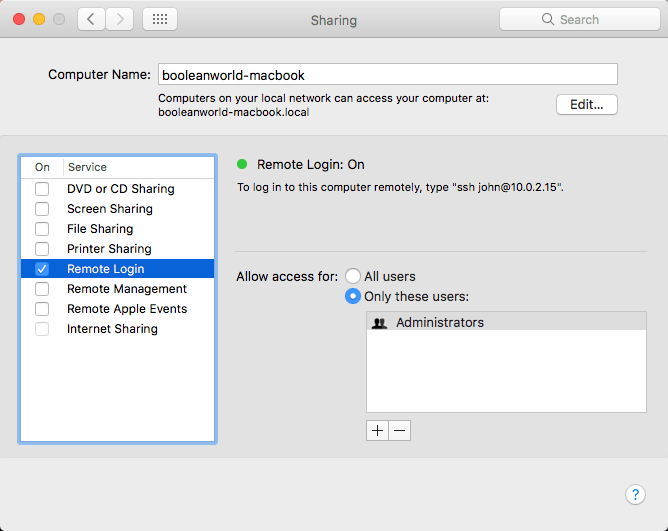
Step 1: Enable SSH on Your Mac
By default, SSH is enabled on macOS. However, you can verify this by checking the system preferences:
Read also:Kannada Movierulz Download 2024 Your Ultimate Guide To Legal And Safe Movie Streaming
- Go to System Preferences > Sharing.
- Check if "Remote Login" is enabled under the Services section.
Step 2: Test SSH Locally
To ensure that SSH is working correctly, you can test it by connecting to your own Mac:
- Open Terminal on your Mac.
- Run the command:
ssh localhost. - Enter your password when prompted.
Connecting to a Remote Server
Once your Mac is prepared, you can connect to a remote server using SSH. Follow these steps:
Basic SSH Command
The basic syntax for connecting to a remote server using SSH is:
ssh username@remote_host
- username: The username of your account on the remote server.
- remote_host: The IP address or domain name of the remote server.
Example
To connect to a server with the IP address 192.168.1.100 and the username "admin," use the following command:
ssh admin@192.168.1.100
Configuring SSH Settings
SSH offers a range of configuration options that allow you to customize your connection settings. These settings can be modified in the SSH configuration file located at ~/.ssh/config.
Common Configuration Options
- Host: Define a nickname for your remote server.
- Port: Specify the port number used for the SSH connection (default is 22).
- IdentityFile: Specify the path to your private key file.
Example Configuration
Here's an example of a basic SSH configuration:
Host myserver
HostName 192.168.1.100
User admin
Port 22
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Advanced SSH Features
SSH offers several advanced features that can enhance your workflow:
SSH Tunnels
SSH tunnels allow you to securely forward traffic between your local machine and a remote server. This is particularly useful for accessing services behind firewalls or encrypting insecure protocols.
SSH Keys
Using SSH keys instead of passwords provides a more secure and convenient way to authenticate your SSH connections. To generate an SSH key pair, use the following command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
Securing Your SSH Connection
While SSH is inherently secure, there are additional steps you can take to further protect your connections:
Disable Password Authentication
By disabling password authentication and requiring SSH keys, you can reduce the risk of brute-force attacks. To do this, edit the SSH server configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshd_config) and set:
PasswordAuthentication no
Use Strong Passwords and Keys
Ensure that your SSH keys are strong and protected with a passphrase. Avoid using weak or default passwords for your accounts.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful preparation, you may encounter issues when using SSH. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Connection Refused
If you receive a "Connection refused" error, ensure that:
- The SSH service is running on the remote server.
- The correct IP address or domain name is used.
- The firewall allows incoming connections on port 22.
Permission Denied
If you encounter a "Permission denied" error, check the following:
- Your username and password are correct.
- The SSH keys are properly configured and accessible.
- The server's SSH configuration allows your connection.
Using SSH for File Transfer
SSH can also be used for secure file transfers using the scp (secure copy) command. Here's how to transfer files:
Copying Files from Local to Remote
To copy a file from your local machine to a remote server:
scp /path/to/local/file username@remote_host:/path/to/remote/directory
Copying Files from Remote to Local
To copy a file from a remote server to your local machine:
scp username@remote_host:/path/to/remote/file /path/to/local/directory
Conclusion and Next Steps
In this comprehensive guide, we've explored how to use SSH remote on Mac without relying on third-party tools. By following the steps outlined, you can securely connect to remote servers, configure advanced settings, and transfer files with ease.
Remember to prioritize security by using strong SSH keys, disabling password authentication, and following best practices for SSH usage. If you encounter any issues, refer to the troubleshooting section for solutions.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may find it useful. For more tips and tutorials, explore our other articles on our website.
References: